Mechanism of action
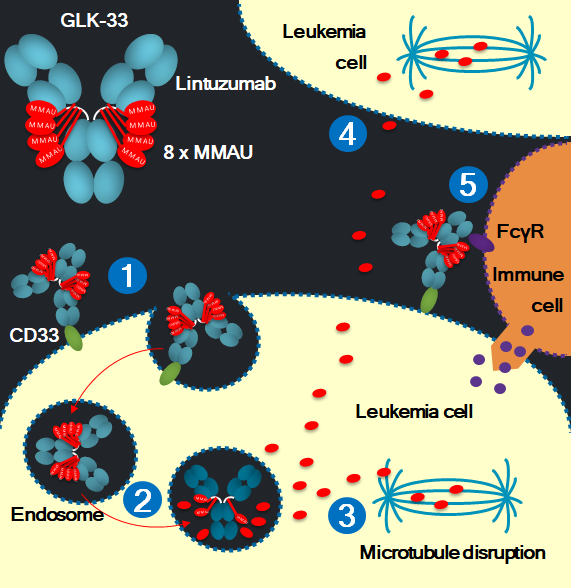
GLK-33 has both payload- and antibody-effector mechanisms
- GLK-33 binds to cell surface CD33 and is internalized into the leukemia cell, leading to receptor blockade and internalization.
- GLK-33 is degraded in the lysosome and the payloads are liberated.
- The active cytotoxic auristatin payload binds to tubulin and causes inhibition of tubulin polymerization and programmed cell death (apotosis).
- The payload can pass through cell membranes and kill bystander leukemia cells.
- Immune cells can bind to the antibody part of GLK-33 on the cell surface with Fc receptors, causing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and immunologic memory against leukemia cells.